Data-driven Decision Making for Social Influence Risk Management
Abstract
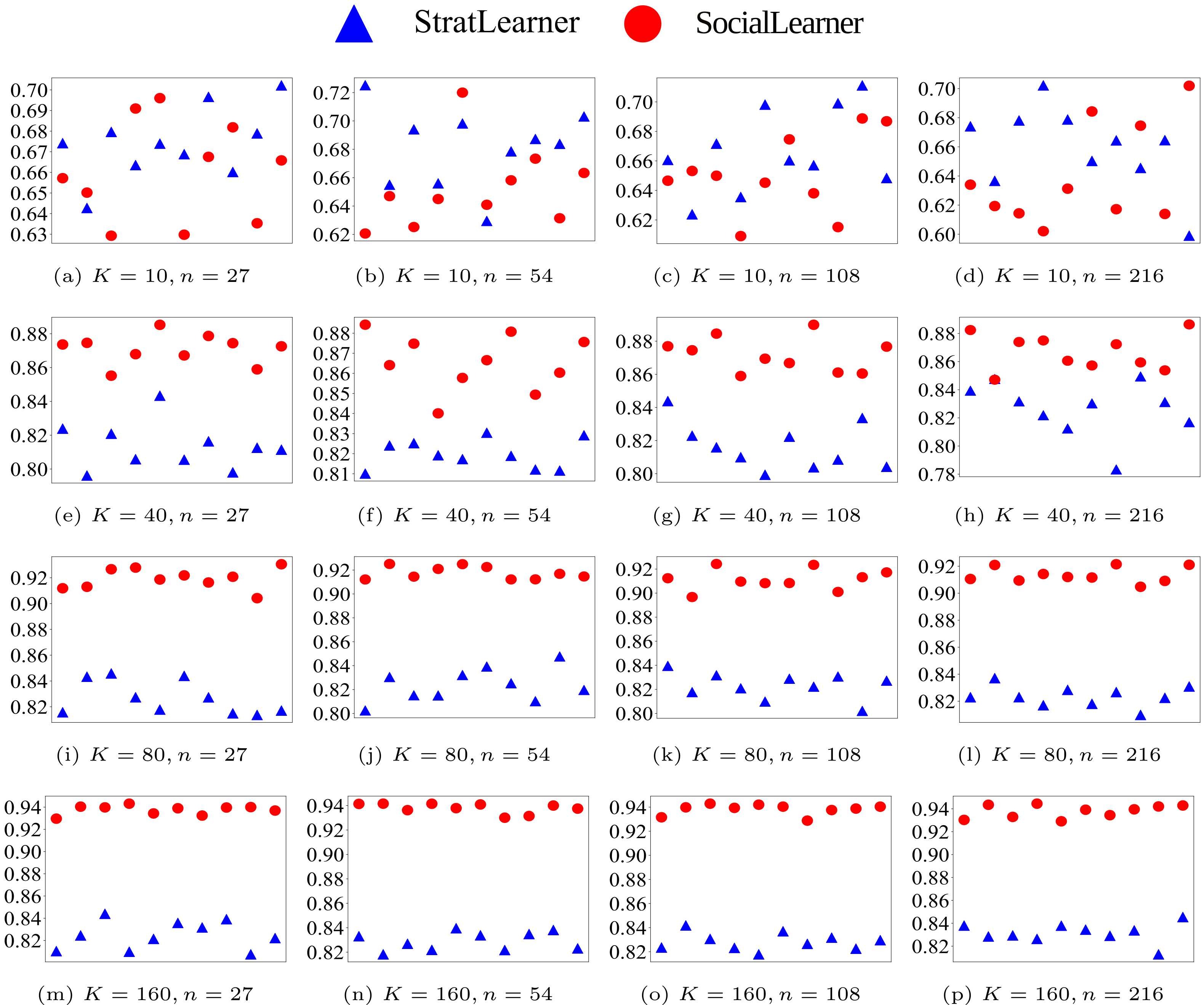
Social influence risk management tasks, such as misinformation prevention and source detection, have gained increasing attention due to the rapid development of social networks, which play an important role in managing the spread of both positive and harmful information. Previous studies for solving these tasks mainly focus on developing exact or approximate approaches where comprehensive diffusion model information is provided. However, it is usually challenging to obtain such information in practice. In this paper, we propose SocialLearner, a novel data-driven decision-making framework designed for social influence risk management tasks in scenarios where diffusion model information is not fully accessible. This approach employs a two-step optimization process that integrates model ensemble techniques with an optimized sampling distribution strategy, aiming to enhance the accuracy of approximating unknown objective functions by leveraging historical pairs of inputs and decisions. Furthermore, extensive experiments on various social influence risk management tasks and network structures are conducted to evaluate the performance of SocialLearner. The results demonstrate its superior accuracy and scalability compared to state-of-the-art methods, highlighting its robustness as a solution in addressing social influence risk management tasks.
Published at: Risk Sciences.
Bibtex
@article{wang2025data, title={Data-driven Decision Making for Social Influence Risk Management}, author={Wang, Siqi and Xie, Jiahao and Wang, Yifan and Tong, Guangmo}, journal={Risk Sciences}, pages={100019}, year={2025}, publisher={Elsevier}}